全密态数据库
可信硬件(TEE)
特性:
密钥管理
索引
TEE计算
1.
the bignum generated by bn_bin2bn needs to be free>
As an AI language model, I don’t have enough context to understand what you’re referring to. Can you please provide more information or context so I can better assist you?
2.
the bignum generated by bn_bin2bn needs to be free?
As a language model, I can infer that you might be referring to the OpenSSL library function bn_bin2bn(), which converts an array of bytes to a BIGNUM (big integer) structure. If that’s the case, then yes, you would need to free the BIGNUM object returned by bn_bin2bn() after you’re done using it to avoid memory leaks. You can do this by calling the BN_free() function on the BIGNUM object.
3.
how to use bn_bin2bn?
bn_bin2bn() is a function provided by the OpenSSL library that converts an array of bytes to a BIGNUM (big integer) structure. Here’s an example of how you can use it:
1 |
|
The BN_bin2bn() function takes three parameters:
If everything goes well, BN_bin2bn() returns a pointer to the BIGNUM object that holds the converted value. Don’t forget to free the BIGNUM object when you’re done with it, using the BN_free() function.
Question :
the third parameter of bn_bin2bn is same to the return value of that function?
Answer :
Share icon
Yes, the third parameter ( BIGNUM *ret ) of the BN_bin2bn() function is used to pass a pointer to a BIGNUM object in which the converted big integer will be stored. If the conversion is successful, the function returns the same pointer as the third parameter, which points to the BIGNUM object.
Here is an example of how you can use BN_bin2bn() and its return value:
1 |
|
In this example, BN_bin2bn() is used to convert the bin byte array into a BIGNUM. The NULL as the third parameter tells the function to create a new BIGNUM object to store the converted big integer. If the conversion is successful, bn will hold the pointer to the new BIGNUM object. After using bn , you should free its memory by calling BN_free(bn) .
Question :
how to use DH_new?
Answer :
Share icon
DH_new() is a function provided by the OpenSSL library that creates a new DH (Diffie-Hellman) key exchange. Here is an example of how to use DH_new() :
1 |
|
The DH_new() function creates a new DH object and initializes it with default values. If the function returns NULL , it means that an error occurred and you should handle it appropriately. Once you’re finished with the DH object, you should free it by calling DH_free(dh) to avoid memory leaks.
4.
how to user “for” in shell?
In shell scripting, a for loop is used for repeating a set of commands for a specified number of times. The syntax of the for loop in shell is as follows:
1 | for variable in list |
Here, variable represents a variable that will take on the value of each item in the list , and command1 , command2 , and so on represent the commands that will be executed for each item in the list .
Here is an example of using a for loop in shell:
1 | !/bin/bash |
This example shows how to loop over a list of files and perform some action on each file. You can modify this example to use your own list of items and commands.
5.
in shell, how to loop n times?
In shell scripting, you can loop a specified number of times using a for loop with a numeric sequence. Here’s an example of how to loop n times in shell:
1 | !/bin/bash |
In this example, we’ve set the value of n to 10, so the loop will execute 10 times. We use the seq command to generate a sequence of numbers from 1 to n and use this sequence in the for loop. You can replace echo “This is loop number $i” with any commands you want to execute in each iteration of the loop.
6.
how to show file context when it is changing in linux shell?
In Linux shell, you can use the tail command with the -f option to view the contents of a file as it changes in real-time. Here’s an example:
1 | tail -f /path/to/file.log |
This command will display the last 10 lines of the file specified by /path/to/file.log and then keep the file open and display any new content that is appended to the end of the file. As new lines are added to the file, they will be displayed in the terminal.
You can use Ctrl + C to stop the tail command and return to the command prompt.
7.
why DH_compute_key error with stack like SLL_next failed?
The error “SLL_next failed” usually occurs when there is an issue with the OpenSSL library’s linked list data structure. This error can occur for several reasons, but most commonly it happens when there is a memory corruption or invalid pointer.
When using DH_compute_key() function in OpenSSL to compute a shared secret key using Diffie-Hellman key exchange, make sure that you have properly initialized the DH object before calling this function. Also, check that both parties have the same DH parameters (p, g, and possibly q) and that their public keys have been exchanged correctly.
If you continue to encounter the “SLL_next failed” error, you may need to debug your code and look for any memory corruption or invalid pointer issues. You can use memory profiling tools like Valgrind to help in this process or consider reviewing and improving your code.
8.
how to find the version of a lib?
To find the version of a library in Linux or Unix-based systems, you can use the ldd command followed by the path to the library file. Here is the syntax for the command:
ldd /path/to/library
When you run this command, it will display the libraries that the specified library depends on, along with their paths. The version of each library should be listed next to the library name.
Alternatively, you can also use the strings command to search for the version string in the library. Here is the syntax for the command:
strings /path/to/library | grep LIBRARY_NAME
Replace LIBRARY_NAME with the name of the library you want to find the version string for. This command will search for all occurrences of the specified library name in the library file and display any version strings that it finds.
9.
how to use DH_generate_key?
DH_generate_key() is a function provided by the OpenSSL library that generates a new Diffie-Hellman key pair. Here is an example of how to use DH_generate_key() with DH_new() :
1 |
|
In this example, DH_new() is used to create a new DH object. DH_generate_key() is then called to generate a new key pair for the DH object. If the function returns a value other than 1 , it means that an error occurred and you should handle it appropriately. Once you’re finished with the DH object, you should free it by calling DH_free(dh) to avoid memory leaks.
After the key pair is generated, you can access the private key using the priv_key member of the DH object and the public key using the pub_key member. For example:
1 | BIGNUM *private_key = dh->priv_key; |
You can then use these keys to perform a Diffie-Hellman key exchange to generate a shared secret key between two parties.
linux shell从键盘获取输入
代码1:
1 | #!/bin/bash |
Redis通常使用字典结构保存用户集合数据, 字典键存储集合元素, 字典值为空. 如果一个集合全是整数, 则使用字典过于浪费内存, 为此, Redis设计了intset数据结构, 专门用来保存整数集合数据
有序集合即数据都是有序的. 存储一组有序收据, 最简单的是一下两种结构:
(1) 数据, 可以通过二分法查找数据, 但插入数据的复杂度为O(n)
(2) 链表, 可以快速插入数据, 但无法使用二分查找, 查找数据的复杂度为O(n)
兼具上面两种结构的优点的数据结构, 跳表skiplist
skiplist是一个多层级的链表结构
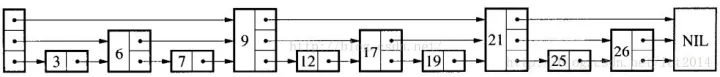
红黑树也常用于维护有序数据, 为什么使用skiplist
Redis4.0之前使用的Hash算法是MurmurHash, 即使输入的键是有规律的, 该算法计算的结果依然有很好的离散性, 并且计算速度非常快. Redis4.0开始更换为SipHash算法, 应该是出于安全的考虑, 该算法能有效防止Hash表碰撞
攻击, 并提供不错的性能
SipHash
大部分非加密哈希算法的改良,都集中在让哈希速度更快更好上。SipHash 则是个异类,它的提出是为了解决一类安全问题:hash flooding。通过让> 输出随机化,SipHash 能够有效减缓 hash flooding 攻击。凭借这一点,它逐渐成为 Ruby、Python、Rust 等语言默认的 hash 表实现的一部分。
如果你愿意尝试下新技术,可以看看 2016 新出的 HighwayHash。它宣称可以达到 SipHash 一样的效果,并且凭借 SIMD 的加持,在运算速度上它是 SipHash 的 5.2 倍(参考来源:https://arxiv.> org/abs/1612.06257 )。
把ht[0]上的数据迁移到ht[1]shang
size调整为2的n次幂, 为了ht[1]Hash表数据长度是ht[0]Hash表数据长度的倍数, 有利于ht[0]的数据均匀地迁移到ht[1]
Hash&ht.sizemask, sizemask=size-1, idx=hash%(ht.size), 因此, 假如ht[0].size为0, ht[1].size=2*n, 对于ht[0]上的元素, ht[0].table[k]的数据, 要不迁移到ht[1].table[k], 要不迁移到ht[1].table[k+n]
执行删除操作后, Redis会检查字典是否需要缩容, 当Hash表长度大于4且负载因子小于0.1时, 会执行缩容操作, 以节省内存
Redis字典使用SipHash算法计算Hash值, 并使用链表法处理Hash冲突
Redis字段使用渐进式扩容方法, 在每次数据操作中都执行一次扩容单步操作, 直到扩容完成
散列类型的编码格式可以为OBJ_ENCODING_HT, OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST